Research
Synthesis and characterization of materials with strong spin-orbit coupling

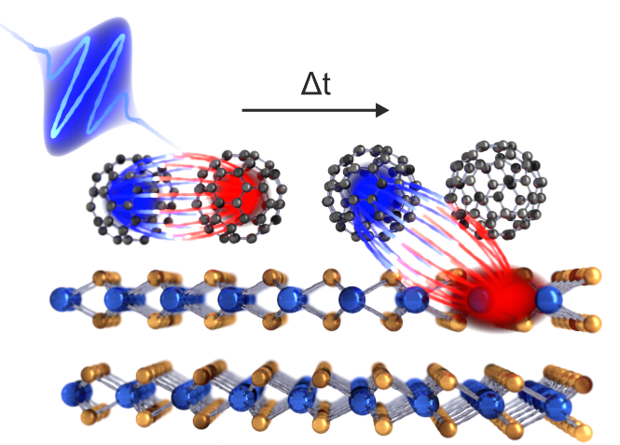
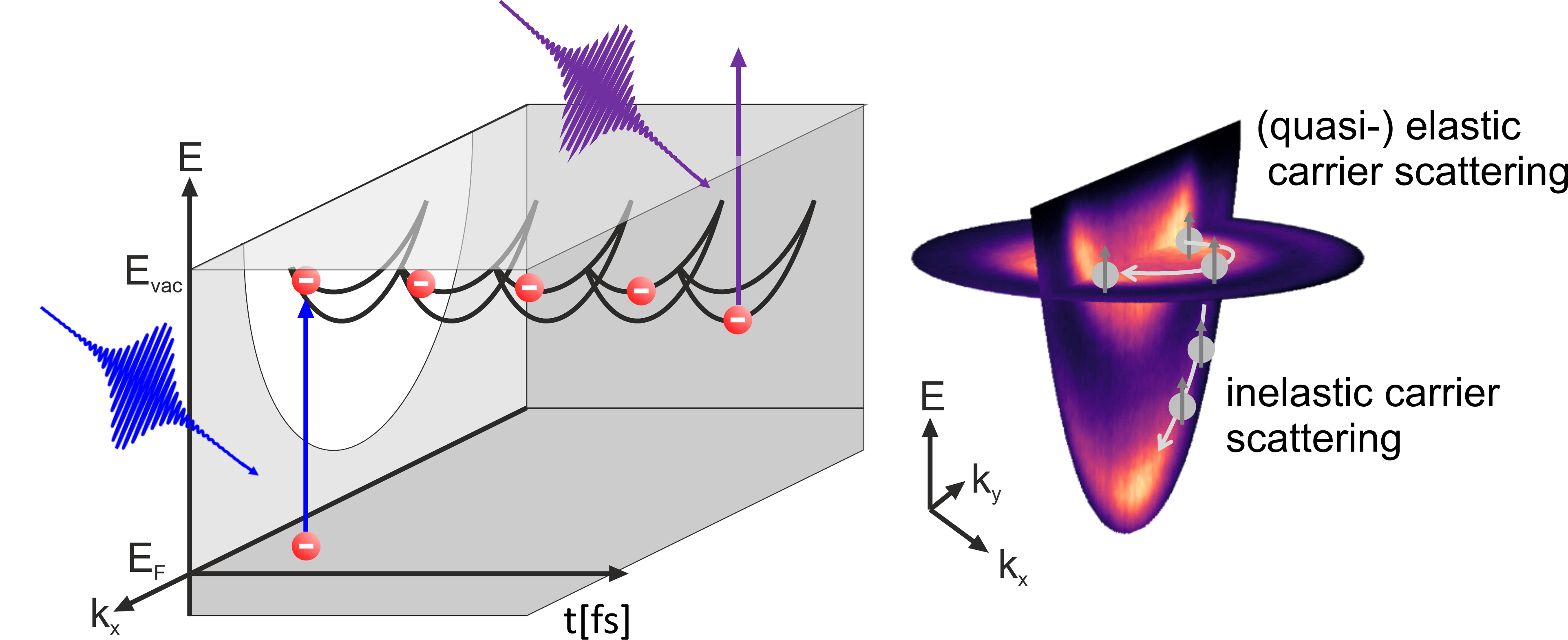
Ultrafast Carrier Dynamics in Low Dimensional Heterostructures
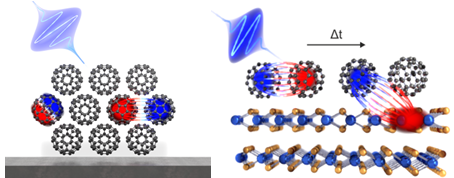
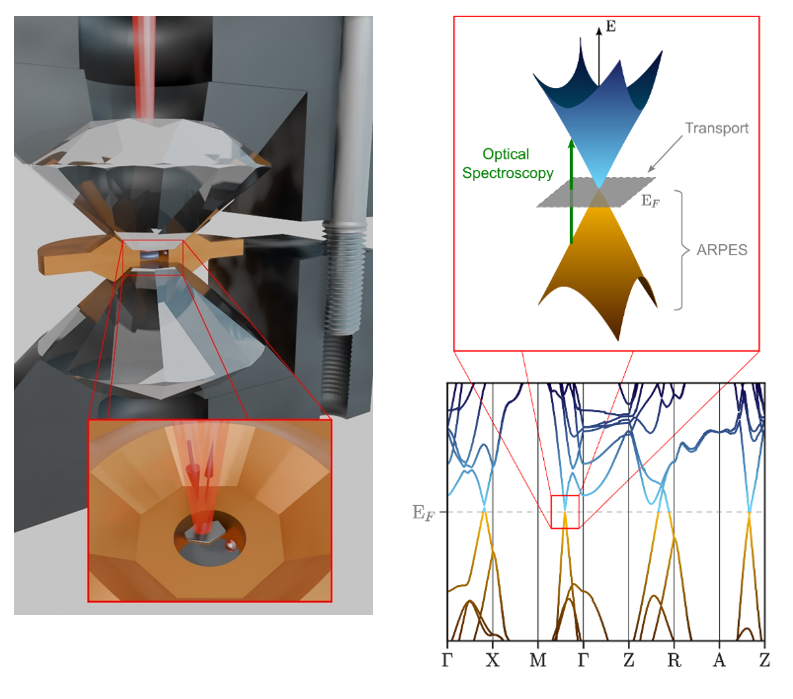
The ultrafast dynamics of charge and spin carriers in solids plays a crucial role in many fundamental and device-relevant phenomena, ranging from light harvesting in molecular and inorganic semiconductors to spin filtering at functional interfaces. In our research, we study the essential energy and (angular) momentum dissipation process of optically excited charge and spin carriers in energy and momentum space on their intrinsic femtosecond to picosecond timescale. This will build the foundation for shaping the spin-dependent materials properties on ultrafast timescales by optical excitation. Currently, we focus on
- the evolution and interconversion of charge transfer and Frenkel excitons in molecular materials
- intersite and interlayer charge and spin transfer processes in molecular and inorganic 2D heterostructures
- momentum dependent lifetimes of quantum-confined electrons in 2D metal-organic porous network structures
For our research, we employ time-, spin- and momentum-resolved photoemission spectroscopy and momentum microscopy. In this pump-probe study, a first femtosecond laser pulse optically excites electrons in the excited state region, while the second probe pulse photoexcites carriers into the vacuum with a well-defined time delay, where they are detected by state-of-the-art photoemission detector systems. For molecular systems, we additionally use the framework of photoemission orbital tomography to gain insight into the spatial distribution of the emitted carriers through their characteristic spectroscopic signatures in momentum space.
Selected Publications:
- Revealing hidden spin polarization in centrosymmetric van der Waals materials on ultrafast timescales
B. Arnoldi, S. L. Zachritz, S. Hedwig, M. Aeschlimann, O. L. A. Monti, and B. Stadtmüller
Nat. Commun. 15, 3573, (2024) - Disentangling the multiorbital contributions of excitons by photoemission exciton tomography
W. Bennecke, A. Windischbacher, D. Schmitt, J. P. Bange, R. Hemm, C. S. Kern, G. D’Avino, X. Blase, D. Steil, S. Steil, M. Aeschlimann, B. Stadtmüller, M. Reutzel, P. Puschnig, G. S. M. Jansen, and S. Mathias
Nat. Commun. 15, 1804 (2024) - Coherent response of the electronic system driven by non-interfering laser pulses
T. Eul, E. Prinz, M. Hartelt, B. Frisch, M. Aeschlimann, and B. Stadtmüller
Nat. Commun. 13, 3324 (2022) - Time-resolved two-photon momentum microscopy—A new approach to study hot carrier lifetimes in momentum space
F. Haag, T. Eul, P. Thielen, N. Haag, B. Stadtmüller, and M. Aeschlimann
Review of Scientific Instruments 90, 103104 (2019) - Strong modification of the transport level alignment in organic materials after optical excitation
B. Stadtmüller, S. Emmerich, D. Jungkenn, N. Haag, M. Rollinger, S. Eich, M. Maniraj, M. Aeschlimann, M. Cinchetti, and S. Mathias
Nat. Commun. 10, 1470 (2019)
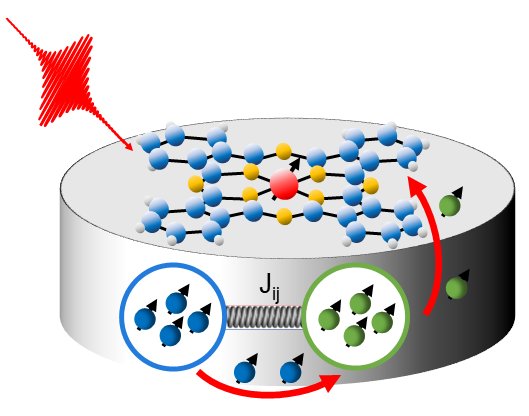
Ultrafast Magnetization Dynamics
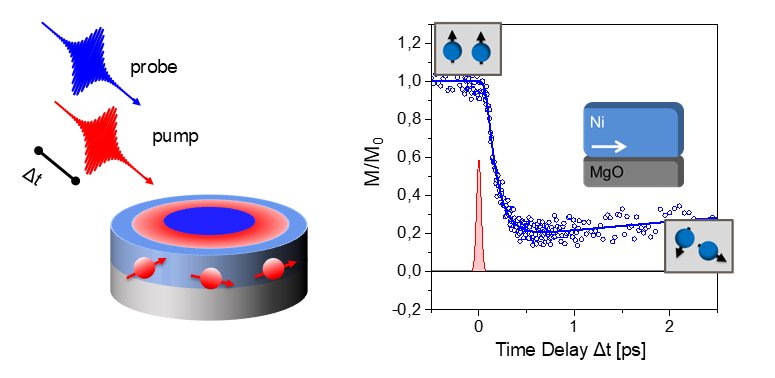
Controlling spin states of condensed matter is a crucial prerequisite for the realization of novel information technology concepts. In our research, we lay the foundation for such efforts by focusing on the ultrafast magnetization dynamics of magnetic materials after optical excitation with femtosecond light pulses. We aim to reveal the microscopic processes governing the ultrafast magnetization dynamics and identify new ways to control the generation of spin-polarized carriers in these materials.
Currently, we focus on
- optically induced intersite and interlayer spin transfer in ferromagnetic alloys and metal-organic hybrid structures
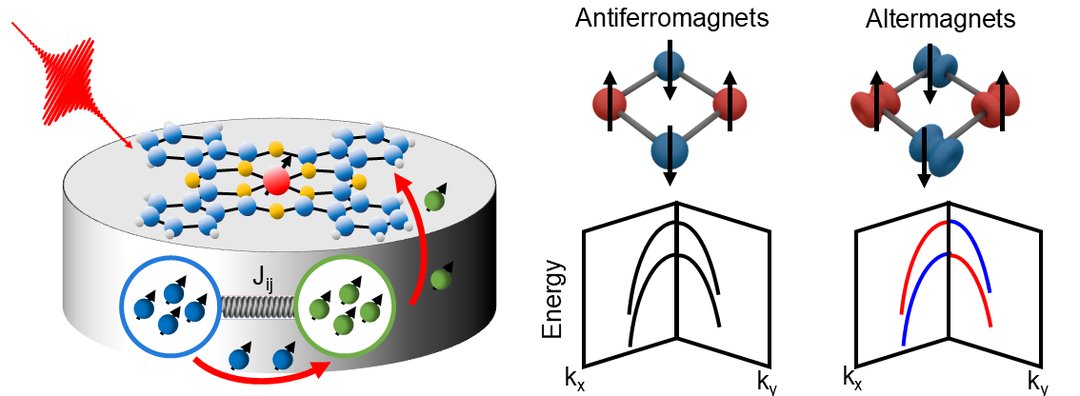
- ultrafast magnetization dynamics in compensated magnets, i.e., in antiferromagnets and altermagnets
For our research, we combine time-, spin- and momentum-resolved photoemission spectroscopy with ultrafast magneto-optics experiments to obtain complementary views on the ultrafast spin-dependent material response of the magnets after optical excitation with fs-light pulses.
Selected Publications and Reprints:
- All optical excitation of spin polarization in d-wave altermagnets
M. Weber, S. Wust, L. Haag, A. Akashdeep, K. Leckron, C. Schmitt, R. Ramos, T. Kikkawa, E. Saitoh, M. Kläui, L. Šmejkal, J. Sinova, M. Aeschlimann, G. Jakob, B. Stadtmüller, H. C. Schneider
arXiv:2408.05187; https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2408.05187 - Observation of time-reversal symmetry breaking in the band structure of altermagnetic RuO2
O. Fedchenko, J. Minár, A. Akashdeep, S. W. D’Souza, D. Vasilyev, O. Tkach, L. Odenbreit, Q. Nguyen, D. Kutnyakhov, N. Wind, L. Wenthaus, M. Scholz, K. Rossnagel, M. Hoesch, M. Aeschlimann, B. Stadtmüller, M. Kläui, G. Schönhense, T. Jungwirth, A. B. Hellenes, G. Jakob, L. Šmejkal, J. Sinova, H.-J. Elmers
Sci. Adv. 10, eadj4883 (2024) - Control of transport phenomena in magnetic heterostructures by wavelength modulation
C. Seibel, M. Weber, M. Stiehl, S. T. Weber, M. Aeschlimann, H. C. Schneider, B. Stadtmüller, B. Rethfeld
Phys. Rev. B 106, L140405 (2022) - Ultrafast spin transfer in ferromagnetic alloys
M. Hofherr, S. Häuser, P. Tengdin, S. Sakshath, H. T. Nembach, S. T. Weber, J. M. Shaw, T. J. Silva, H. C. Kapteyn, M. Cinchetti, B. Rethfeld, M. M. Murnane, D. Steil, B Stadtmüller, S. Sharma, M. Aeschlimann, S. Mathias
Sci. Adv. 6 eaay8717 (2020) - Band structure evolution during the ultrafast ferromagnetic-paramagnetic phase transition in cobalt
S. Eich, M. Plötzing, M. Rollinger, S. Emmerich, R. Adam, C. Chen, H. C. Kapteyn, M. M. Murnane, L. Plucinski, D. Steil, B. Stadtmüller, M. Cinchetti, M. Aeschlimann, C. M. Schneider, S. Mathias
Sci. Adv. 3 (3), e1602094 (2017)
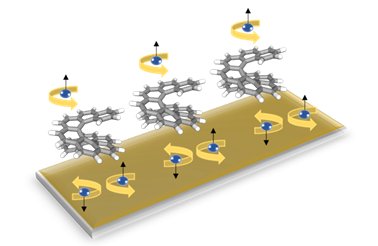
Spin Functionalities in Molecular Hybrid Structures
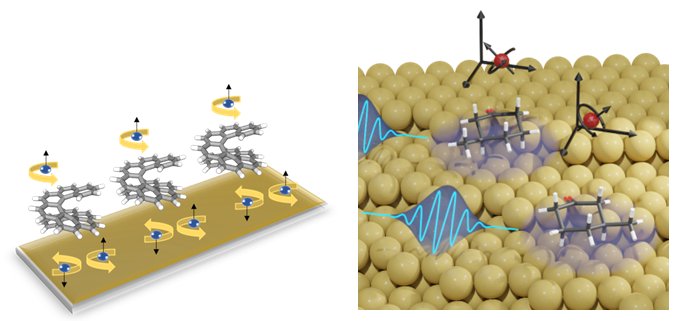
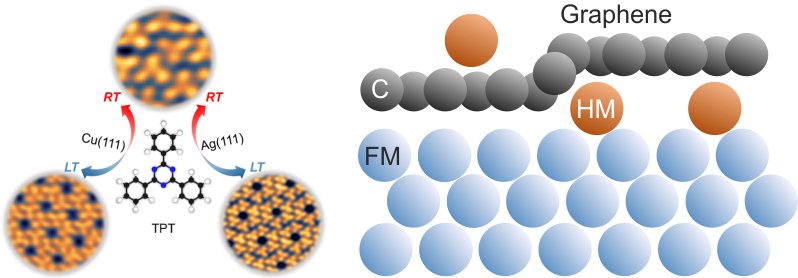
Molecular materials on surfaces are a fascinating construction kit for controlling spin functionalities such as spin filtering and spin diffusion on the nanoscale. However, tuning such spin functionalities requires an in-depth understanding of the delicate balance of the intermolecular and molecule-surface interactions in molecular-based hybrid structures typically reflected by the arrangement of the molecular superstructures. In our research, we, therefore, focus on the link between the efficiency of spin functionalities and the structural order of molecular–surface hybrid structures. Currently, we focus on
- chirality-induced spin filtering in chiral metal-molecular hybrid structures
- spin-polarization of quantum confined surface electrons in tailored metal-organic networks
- spin filtering in bare and passivated magnetic metal-molecule hybrid structures
For our investigations, we combine structural characterization tools such as scanning tunneling microscopy and the synchrotron-based normal-incidence X-ray standing waves technique with spin-resolved electron spectroscopy tools to obtain a comprehensive view of the interactions and corresponding spin functionalities in molecular hybrid structures.
Selected Publications:
- Vectorial Electron Spin Filtering by an All-Chiral Metal–Molecule Heterostructure
C. B. Viswanatha, J. Stöckl, B. Arnoldi, S. Becker, M. Aeschlimann, B. Stadtmüller
J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 6244–6249 - Observation of optical coherence in a disordered metal-molecule interface by coherent optical two-dimensional photoelectron spectroscopy
M. Aeschlimann, T. Brixner, M. Cinchetti, M. Feidt, N. Haag, M. Hensen, B. Huber, T. Kenneweg, J. Kollamana, C. Kramer, W. Pfeiffer, S. Ponzoni, B. Stadtmüller, P. Thielen
Phys. Rev. B 105, 205415 (2022) - Thermal-Driven formation of 2D Nanoporous Networks on Metal Surfaces
L. Lyu, M. Mahalingam, S. Mousavion, S. Becker, H. Huang, M. Aeschlimann, B. Stadtmüller
J. Phys. Chem. C 123, 26263-26271 (2019) - Spin- and Angle-Resolved Photoemission Study of the Alq3/Co Interface
J. Stöckl, A. Jurenkow, N. Großmann, M. Cinchetti, B. Stadtmüller, M. Aeschlimann
J. Phys. Chem. C 122 (12), 6585–6592 (2018) - Modifying the Surface of a Rashba-Split Pb-Ag Alloy Using Tailored Metal-Organic Bonds
B. Stadtmüller, J. Seidel, N. Haag, L. Grad, C. Tusche, G. van Straaten, M. Franke, J. Kirschner, C. Kumpf, M. Cinchetti, M. Aeschlimann
Phys. Rev. Lett. 117, 096805 (2016)
Tuning topological electronic states by external pressure
In recent years, the investigation of topological phases in condensed matter has attracted a lot of interest. Prominent examples are the Dirac and Weyl semimetal phases, where linear band crossings (forming Dirac/Weyl cones) occur near the Fermi energy EF. Interband transitions in Dirac/Weyl cones lead to a characteristic shape of the optical conductivity spectrum, following a distinct power-law according to σ1(ω) ∝ ωd−2, depending on the dimensionality d of the Dirac fermions.
Among the Dirac materials, the family of kagome lattice compounds has sparked tremendous research efforts due to a plethora of interesting phases and phenomena: flat bands, Dirac states, and van Hove singularities (VHSs) in the electronic band structure, charge-density-wave (CDW) and unconventional superconducting phases, magnetic order, orbital selective nematic order or electronic nematicity, fractional quantum Hall physics, and Kondo effect. Kagome materials thus offer an ideal playground to study the interplay between geometry, topology, and electron correlations as well as the interrelation between CDW and superconductivity (SC) or magnetism.
We also study the square-net lattice materials LnSbTe (Ln=rare earth element), which host a magnetic topological nodal-line semimetallic state at low temperatures. Suitable substitution and vacancy concentration cause structural distortion and the development of CDWs in LnSbxTe2−x− compounds, which enables an electronic band engineering and can generate novel topological phases.
For our research, we apply infrared and Raman spectroscopy to characterize the charge and lattice dynamics in Dirac materials. Combined with external pressure applied by diamond anvil cells, we can monitor the optical response while tuning the electronic bandwidth, unveiling pressure-induced electronic and structural phase transitions.
Selected publications:
- Optical anisotropy of the kagome magnet FeSn: dominant role of excitations between kagome and Sn layers
J. Ebad-Allah, M.-C. Jiang, R. Borkenhagen, F. Meggle, L. Prodan, V. Tsurkan, F. Schilberth, G.-Y. Guo, R. Arita, I. Kézsmárki, C. A. Kuntscher
Phys. Rev. B 109, L201106 (2024) - Optical signatures of type-II Weyl fermions in the noncentrosymmetric semimetals RAlSi (R = La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm)
J. Kunze, M. Köpf, W. Cao, Y. Qi C. A. Kuntscher
Phys. Rev. B 109, 195130 (2024) - Pressure-induced excitations in the out-of-plane optical response of the nodal-line semimetal ZrSiS
J. Ebad-Allah, S. Rojewski, M. Vöst, G. Eickerling, W. Scherer, E. Uykur, R. Sankar, L. Varrassi, C. Franchini, K.-H. Ahn, J. Kuneš, C. A. Kuntscher
Phys. Rev. Lett. 127, 076402 (2021) - Indications for Lifshitz transitions in the nodal-line semimetal ZrSiTe induced by interlayer interaction
M. Krottenmüller, M. Vöst, N. Unglert, J. Ebad-Allah, G. Eickerling, D. Volkmer, J. Hu, Y. L. Zhu, Z. Q. Mao, W. Scherer, C. A. Kuntscher
Phys. Rev. B 101, 081108(R) (2020)
Pressure-induced phase transitions in 2D van der Waals materials
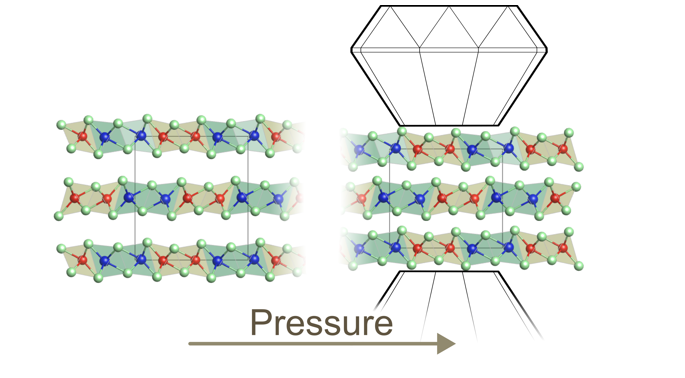
Layered van der Waals materials exhibit a plethora of interesting physical properties and exotic phases due to competing correlation effects and topology, such as charge-density wave, Mott insulator, superconductivity, antiferromagnetic topological insulator, Weyl semimetal, and ferromagnetic nodal-line semimetal. Furthermore, they provide an ideal platform for realizing atomically thin crystals with unique properties and excellent prospects for novel applications. For the understanding of the physical properties of these novel 2D crystals, the characterization and understanding of their bulk physical properties are crucial as a preliminary step and are the subject of this project. One key aspect determining the physical properties of two-dimensional, layered materials is the interlayer interaction. In particular, the variation of the interlayer interaction by changing the van der Waals interlayer spacing greatly affects their physical properties and induces phase transitions with emerging exotic phases. The systematic study and understanding of the influence of the interlayer interaction on the charge and lattice dynamics in layered van der Waals materials are the goal of this project. External pressure is the most effective way for tuning the interlayer spacing and hence the interlayer interaction in a controlled manner. Hence, external pressure will be applied within this project to systematically investigate the influence of interlayer interaction on the optical response of various van der Waals materials.
Prominent examples of our study include the topological insulator MnBi2Te4, the ferromagnet CrGeTe3, and the type II-Weyl semimetals (Nb,Ta)IrTe4.
Selected publications:
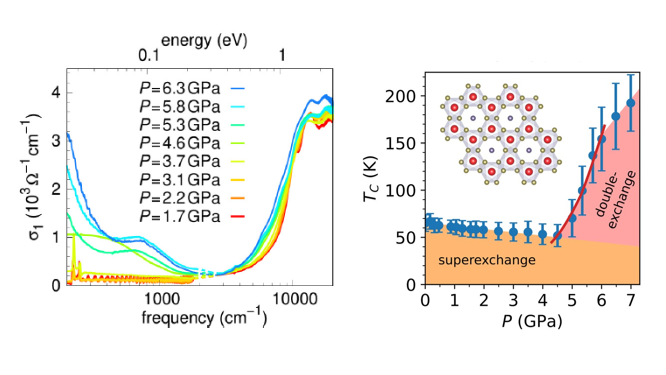
- Near room-temperature ferromagnetism from double exchange in the van der Waals material CrGeTe3: evidence from optical conductivity under pressure
J. Ebad-Allah, D. Guterding, M. Varma, M. Diware, S. Ganorkar, H. O. Jeschke, C. A. Kuntscher
Phys. Rev. B 111, L140402 (2025) - Optical study of the charge dynamics evolution in the topological insulators MnBi2Te4 and Mn(Bi0.74Sb0.26)2Te4 under high pressure
M. Köpf, S. H. Lee, Z. Q. Mao, C. A. Kuntscher
Phys. Rev. B 109, 245124 (2024)
Synthesis and characterization of materials with strong spin-orbit coupling
The pyrochlore iridates R2Ir2O7 (R = rare-earths, Y and Bi), being the three-dimensional analogue of the kagome structure, have been predicted to host novel topological phases. The corner-sharing tetrahedral network of the pyrochlore lattice naturally gives rise to strong geometrical frustration, which suppresses conventional magnetic ordering and favors the emergence of unconventional ground states. Generally, iridates have been extensively investigated in the last years because of the interplay of Coulomb interaction, spin-orbit coupling, crystal field splitting, and electronic bandwidth, all with comparable energy scales. Their delicate balance induces novel phases and promotes the possible realization of the quantum spin-liquid ground state. In particular, a Weyl semimetal phase has been proposed for the magnetic pyrochlores A2Ir2O7 (A = Y, Eu, Sm and Nd) in their antiferromagnetic state with all-in/all-out spin order, which preserves inversion symmetry but breaks time-reversal symmetry.
We employ the flux-growth method to obtain high-quality single crystals of pyrochlore iridates. The crystals are characterized using energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, dc electrical transport, magnetic susceptibility, heat capacity, Raman spectroscopy, and infrared spectroscopy. Crystal synthesis is carried out in close collaboration with Anton Jesche and Philipp Gegenwart, Experimental Physics VI.
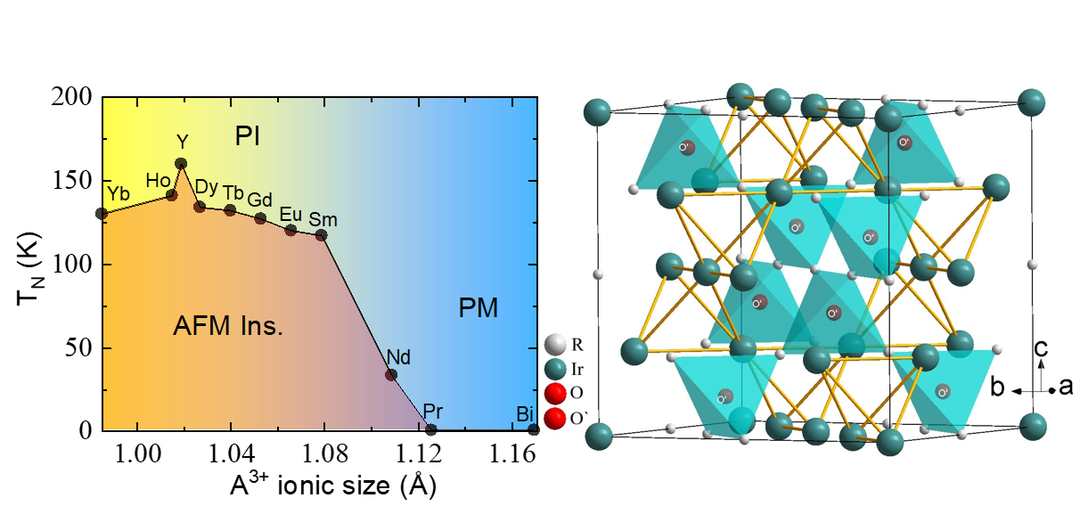

Selected publications:
- Magnetic and transport properties in pyrochlore iridates (Y1-xPrx)2Ir2O7: The role of f-d exchange interaction and d-p orbital hybridization
H. Kumar, K. C. Kharkwal, K. Kumar, K. Asokan, A. Banerjee, A. K. Pramanik
Phys. Rev. B 101, 064405 (2020) - Optical Conductivity of metallic Pyrochlore Iridate Pr2Ir2O7: Influence of Spin-Orbit and Electron-Electron Interactions on the electronic structure
H. Kumar, M. Köpf, P. Telang, N. Bura, A. Jesche, P. Gegenwart, C. A. Kuntscher
Phys. Rev. B 110, 035140 (2024)