Modeling Network Load of Mobile Instant Messaging: A Modular Source Traffic Generator
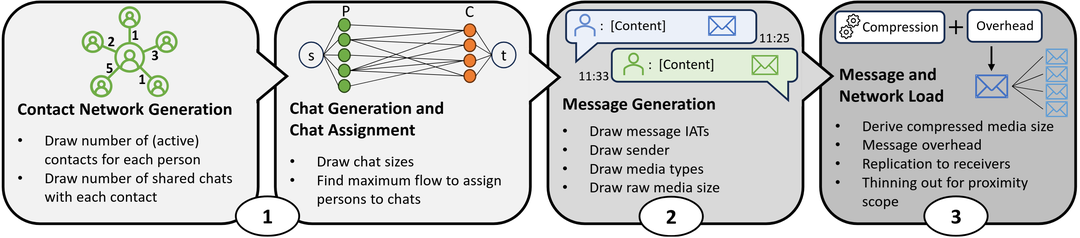
Our article entitled “Modeling Network Load of Mobile Instant Messaging: A Modular Source Traffic Generator,” written by our chair in collaboration with researchers from the University of Würzburg, was recently accepted for publication in the IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management journal. This paper investigates how Mobile Instant Messaging (MIM) traffic can be effectively modeled to support network planning. While apps like WhatsApp enable global exchange of text, images, videos, and voice messages, they impose high network load, especially in group chats. End-to-end encryption prevents direct observation of message flows, requiring alternative modeling approaches. We present a modular Source Traffic Modeling (STM) approach for MIM, identifying its key building blocks and addressing gaps through studies on communication patterns, contact proximity, media compression, and file size distributions. By combining literature and empirical data, the STM framework is implemented and used to estimate daily network traffic per user. This research demonstrates how structured traffic modeling can improve network understanding and guide future network design for encrypted MIM services. Paper: Fabian Poign´ee, Anika Seufert, Frank Loh, Michael Seufert, Tobias Hoßfeld. "Modeling Network Load of Mobile Instant Messaging: A Modular Source Traffic Generator." IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management Journal. Link to paper:
Modeling Network Load of Mobile Instant Messaging: A Modular Source Traffic Generator